Controlling Emissions in Power Plants
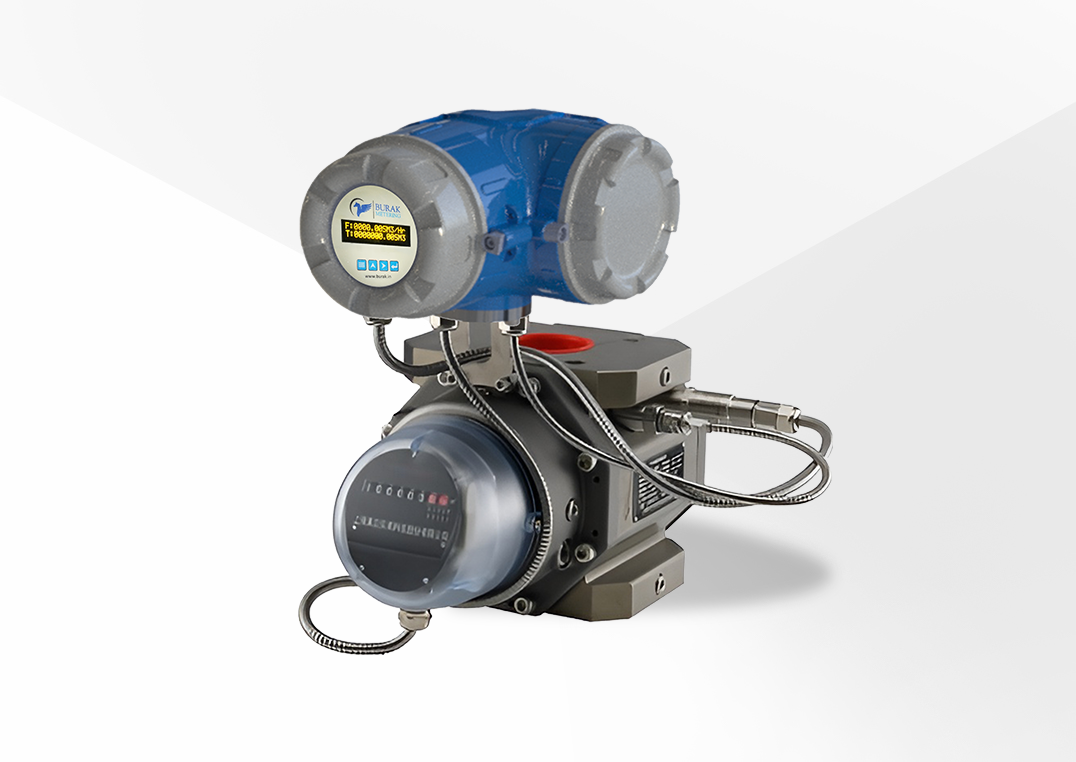
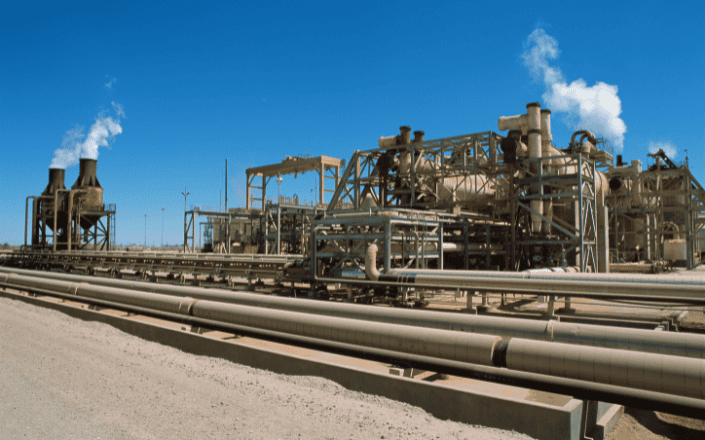
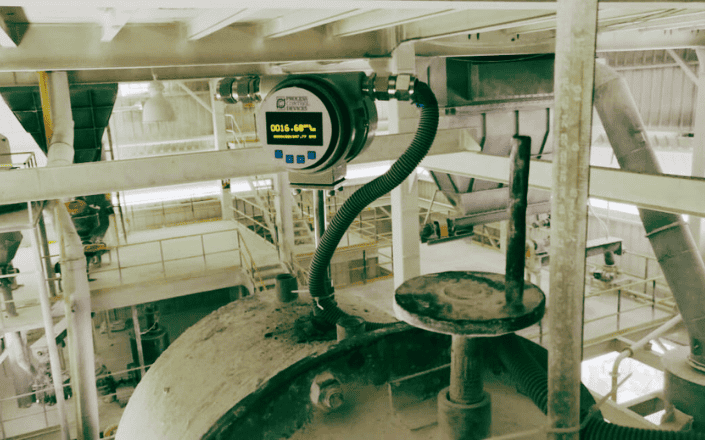
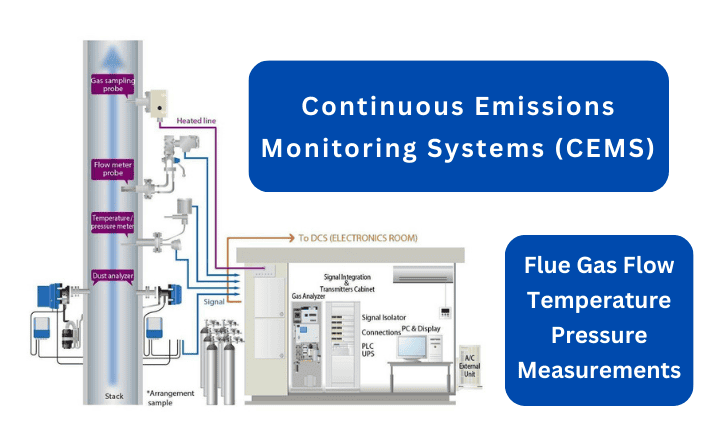
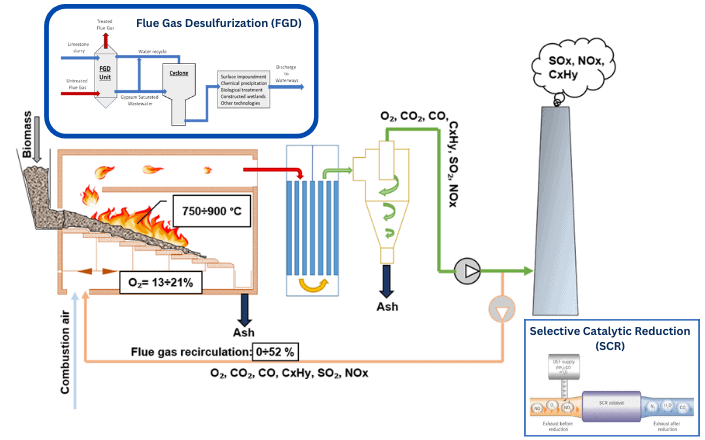
Controlling emissions in power plants is a crucial responsibility, driven by the necessity to mitigate environmental impact and comply with stringent regulations. This process involves the management and reduction of pollutants released during power generation. Power plants utilize various methods to control emissions, especially those of harmful gases and particulate matter. One primary approach is installing emission control systems like scrubbers, filters, and electrostatic precipitators. These systems help capture and remove pollutants from flue gases before they are released into the atmosphere. Committing to reducing emissions involves a multi-faceted approach, integrating technological advancements, stringent regulatory compliance, and a shift towards cleaner energy sources. By implementing and improving these emission control measures, power plants aim to minimize their environmental footprint while continuing to meet the growing electricity demand.