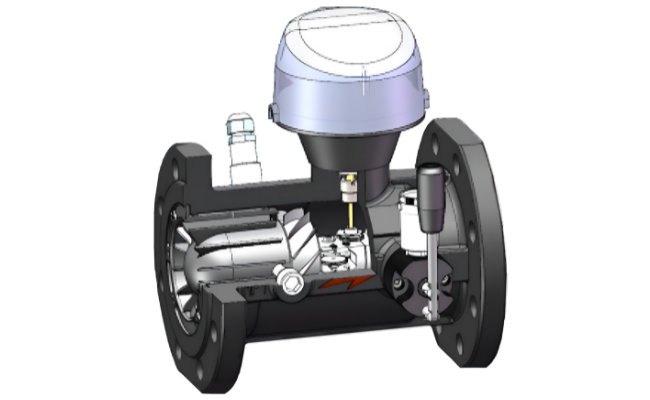
Working Principle of turbine gas meter
The turbine gas meter operates by measuring the velocity of the gas flow. The gas enters the meter and passes through a turbine rotor, causing it to spin.
Turbine Rotation and Signal Generation:
The speed of the turbine rotor is directly proportional to the flow rate of the gas. This rotational speed is converted into an electronic signal, which represents the volumetric flow rate.
Electronic Volume Corrector (EVC):
The EVC enhances the accuracy of the measurement by compensating for variations in temperature and pressure. Sensors integrated with the EVC monitor real-time gas temperature and pressure conditions. The EVC applies correction algorithms to calculate the normalized or corrected gas volume, typically referenced to standard temperature and pressure.
Output Integration:
The meter provides an analog output signal (4-20mA), enabling seamless integration with control systems, SCADA, or other data acquisition platforms.
Reliable Performance Under Fluctuating Conditions:
The turbine gas meter combined with the EVC ensures precise and consistent gas flow measurement, even when operating conditions vary significantly.
This combination of turbine technology and electronic correction makes the turbine gas meter with EVC ideal for applications requiring high accuracy, reliability, and adaptability in gas flow measurement.
Applications of Turbine Gas Meter
Our Turbine Gas Meter is used in the following industries and applications:
- Natural Gas Distribution (CGD networks)
- Power generation plants (fuel gas lines)
- Industrial gas usage (chemical plants, refineries, steel, cement)
- LPG / Propane / Butane pipelines
- Non-corrosive gases in process industries
Benefits for industry:
- Low pressure drop means less energy loss and stable process.
- High repeatability means reliable data for cost tracking or billing.
- Long service life means low maintenance and downtime.
How to Choose the Right Turbine Gas Meter?
To pick the correct meter, consider:
- Pipe size and fluid flow: Make sure the meter’s DN size and Qmin-Qmax match your pipeline and gas flow rate.
- Gas type & condition: Ensure the gas is clean, free from dust/particles/moisture, as these can affect the rotor.
- Pressure & temperature: Know your operating pressure & temperature; if they vary widely you may need the EVC version for corrected volume.
- Installation straight-run & flow profile: Turbine meters require certain lengths of straight pipe upstream/downstream to give accurate readings (avoid disturbed flow).
- Accuracy & rangeability: For billing or critical measurement, higher accuracy and wide rangeability matter.
- Integration & output: Decide on the type of output you need (pulse, 4-20 mA, RS-485) and whether you will integrate with SCADA or control system.
- Service & calibration: Check that the manufacturer can calibrate or service the meter in India.
Need help? Contact us now with your gas type, flow rate, pipe size and we’ll guide you.