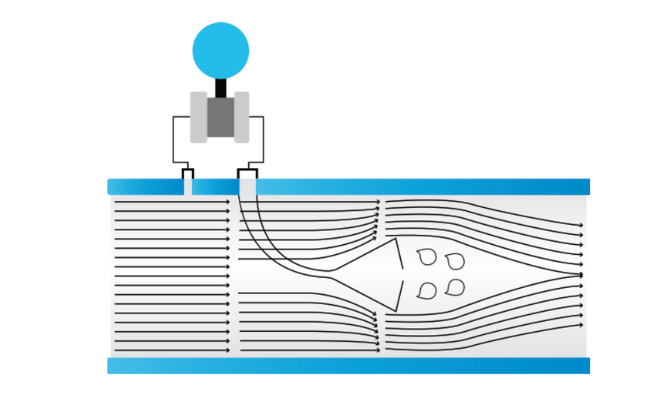
Working Principle
The cone flow meter operates based on the principle of differential pressure measurement, which involves the following steps:
Flow Obstruction: A centrally located cone is placed within the flow path inside the pipe. As fluid (liquid or gas) flows through the pipe, it encounters the cone.
Pressure Differential Creation: The presence of the cone causes the fluid to accelerate around it, creating a high-pressure region upstream of the cone and a low-pressure region downstream of the cone.
Pressure Measurement: The differential pressure (the difference between the upstream and downstream pressures) is measured using pressure taps located before and after the cone.
Flow Rate Calculation: The differential pressure is proportional to the square of the flow rate. By applying Bernoulli's equation and the continuity equation, the flow rate can be calculated accurately from the measured pressure differential using ISO 5167 Part 5 published equations.
Output and Display: The calculated flow rate can be transmitted to a flow computer or display unit for monitoring and control purposes.
The cone flow meter's design ensures stable and accurate pressure measurements, making it suitable for a wide range of flow measurement applications, even with fluids that contain particulates or have varying viscosity.