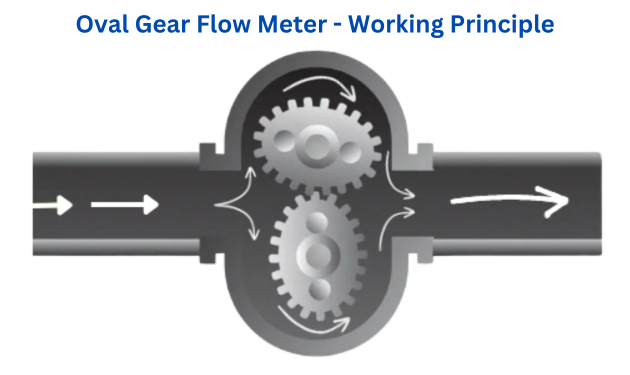
Working Principle of Oval Gear Flow Meter
The working principle of an oval gear flow meter revolves around the concept of positive displacement. It measures the flow rate of liquids by utilizing a pair of precisely machined oval gears within a chamber.
Flow Passage: Liquid flows through the chamber that houses the meter's gears.
Gearing Mechanism: Inside this chamber, two oval-shaped gears mesh together. These gears have a specific number of teeth and are designed to fit snugly within the chamber, forming a seal between the inlet and outlet.
Liquid Displacement: As the liquid flows through the chamber, it enters the spaces between the rotating oval gears. The gears rotate due to the force exerted by the flowing fluid.
Volume Measurement: Each rotation of the gears displaces a fixed volume of liquid. The volume of fluid passing through the meter is directly proportional to the number of gear rotations.
Sensor or Counter: The rotation of the gears is typically detected by sensors or counters integrated into the meter. These sensors generate electrical signals or mechanical movements that are then translated into flow rate measurements.
Output: The flow rate data is displayed on an attached gauge or transmitted to a control system for monitoring or further processing.
This method provides highly accurate measurements regardless of the liquid's viscosity, as the gears displace a consistent volume per rotation. Oval gear flow meters excel in accurately measuring low flow rates. They are suitable for various liquids, from thin to highly viscous substances, making them a reliable choice in various industrial applications.